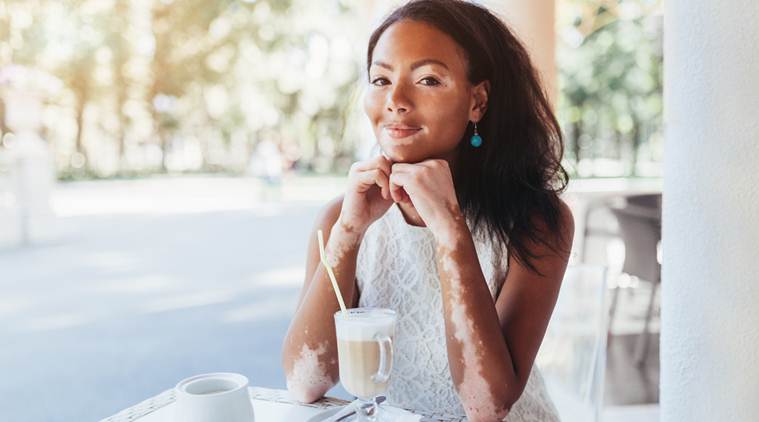
A skin disease in which pale white patches start forming on the skin, vitiligo is caused due to lack of melanin, a pigment in the skin. Every year, June 25 is observed as World Vitiligo Day to raise awareness about the condition. The international theme for this year is ‘The Quality of Life of a Vitiligo Patient’, and the campaign will focus on mental and medical journey of vitiligo.
Dr Binita Priyambada, senior consultant, medical team at Docprime.com explains the condition and also shares the symptoms and treatment for the same.
“People with vitiligo not only suffer from its symptoms but also face social and emotional hurdles. The only way we can mitigate these challenges is by making ourselves aware. There are few important things that we should know about this rare condition,” she says.
What is vitiligo?
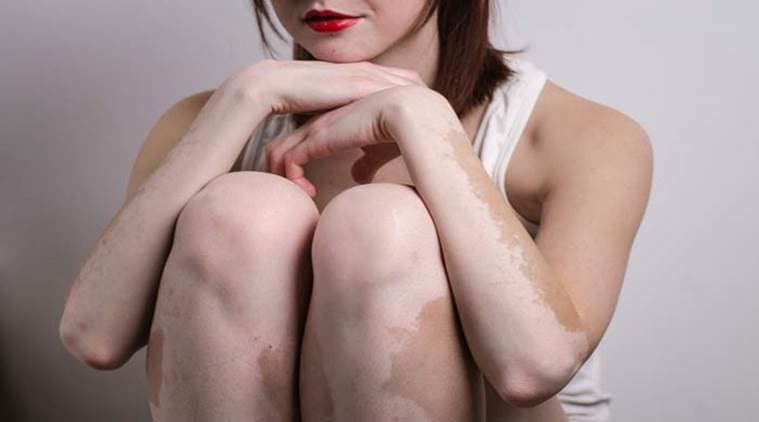

Vitiligo is a skin disease where pale white patches start forming on the skin due to lack of melanin, a skin pigment. Almost 1-2 per cent of the population across the globe suffer from this condition, which is rare and often met with misconceptions. One of the most common misconceptions is that vitiligo is contagious — however, it is essential to note that the condition is not contagious and does not spread from getting in direct contact with the affected person.
Medical research has not found a particular cause for this autoimmune disorder. The possibilities of vitiligo occurring due to genetic conditions or stress-induced situations are very likely to hold true. Vitiligo can affect any area of the skin but it is most commonly observed on the face, neck, arms and skin creases. The pale area of the skin is extremely prone to sunburn, which is why it is essential to take care of it.
Certain triggers that can make it worse:
Both genetic and environmental factors can lead to the worsening of this condition. But there are certain triggers that are associated with this occurring. Potential triggers include:
*UV radiations that come from sun, tanning bed, wielding torches, mercury lamps
*Exposure to certain chemicals
*Stress

Risk factors:
Apart from white patches forming on the skin, there are certain other risk factors associated with this disorder. These include:
*Inflammation in the iris
*Loss of hearing
*Sunburn
Symptoms:
Vitiligo commonly manifests in people in their twenties; however, it can occur in any stage. People with autoimmune diseases, such as hyperthyroidism are more prone to it than those who don’t have any autoimmune diseases. The symptoms of vitiligo are categorised on the basis of segmentation.
Non-Segmental Vitiligo: Symptoms in this case appear on both sides of your body as symmetrical white patches. Areas affected by non-segmental vitiligo include:
*Back of your hands
*Arms
*Skin around body openings/creases
*Feet
*Elbows
*Knees
Segmental Vitiligo: Segmental or localised vitiligo affects only one area of your body. Segmental vitiligo is less common in comparison to non-segmental vitiligo. It usually affects children and is found in three out of 10 children affected by vitiligo.
Treatment:
Treatment of vitiligo can vary depending on the kind of treatment the specialist finds suitable, the vastitude (number of patches and how prevalent they are) of the condition and the patient’s outlook.
Most common medical treatments include:
*Medicated creams and ointments for skin
*Oral medicines
*Medicine and phototherapy as a combined treatment
*Surgical treatments like – skin grafts and tattooing small areas of skin
*Sunscreens
*Counselling and support
Treatment options of vitiligo are largely dependent on its progress. If a few skin patches stay stable for a year and no new patches come up, surgery is a good option. However, if the patches keep growing or new patches keep appearing, phototherapy or medical therapy are the options. There is good response in majority of cases at least for a while. Therefore, instead of despairing, patients should take sound medical advice and follow up on treatment suggested.
[“source=indianexpress”]